Many people confuse a heart attack with cardiac arrest, but these are two very different medical emergencies. In this article, we break down heart attack vs cardiac arrest, explain how they differ, and what immediate actions can save lives.
Heart Attack vs Cardiac Arrest: Key Differences
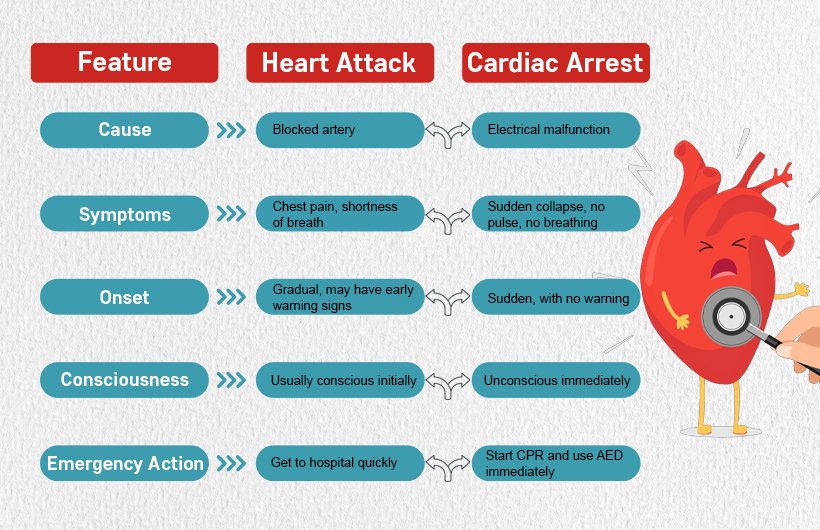
Although both conditions affect the heart, the difference between a heart attack and cardiac arrest lies in how they occur and how they impact the body.
A heart attack occurs when blood flow to part of the heart is blocked, often due to a clogged artery. In contrast, cardiac arrest happens when the heart suddenly stops beating due to a problem with its electrical system.
What Is a Heart Attack?
Heart attack symptoms and causes are often linked to lifestyle, diet, and existing health conditions. A heart attack (myocardial infarction) typically occurs when one or more coronary arteries become blocked, reducing blood flow to the heart muscle.
Common Causes:
- Coronary artery disease
- High cholesterol or high blood pressure
- Smoking or excessive alcohol
- Sedentary lifestyle
Symptoms:
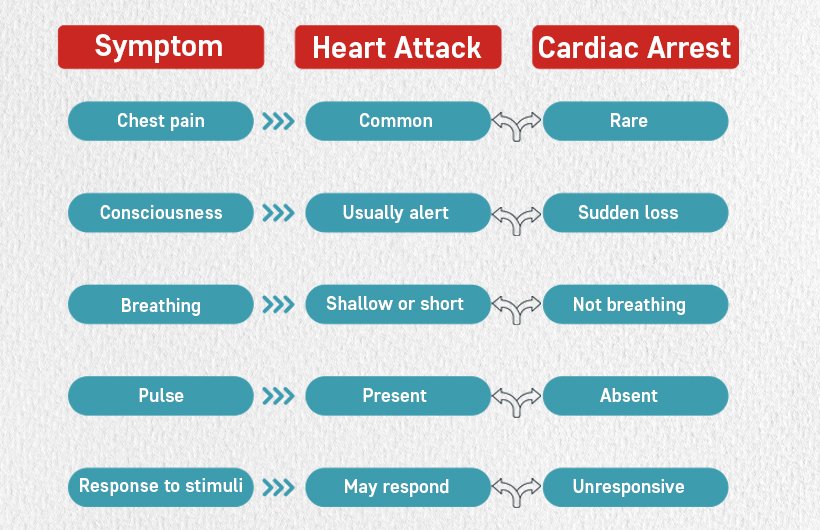
- Chest discomfort or pressure
- Pain in arms, back, jaw, or stomach
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea, sweating, lightheadedness
If you or someone experiences these symptoms, it’s crucial to seek heart attack treatment immediately.
What Is Cardiac Arrest?
For a clearer sudden cardiac arrest, it helps to know that this condition is electrical. The heart suddenly stops beating effectively, which halts blood flow to the brain and other vital organs.
Common Causes:
- Arrhythmias like ventricular fibrillation
- Heart failure
- Severe trauma or drowning
- Genetic heart conditions
Symptoms:
- Sudden collapse
- No breathing
- No pulse
- Loss of consciousness
Unlike a heart attack, sudden cardiac arrest vs heart attack typically leaves no time for response unless CPR and defibrillation are started immediately.
Heart Attack vs Cardiac Arrest Symptoms
Understanding the symptom differences can mean the difference between life and death. Here’s a quick comparison:
Emergency Response: What to Do
Knowing what to do can save a life in both emergencies.
1. For a Heart Attack:
- Call emergency services immediately.
- Keep the person calm and seated.
- If prescribed, administer nitroglycerin or aspirin.
- Get to a Heart Hospital in Ahmedabad as quickly as possible.
2. For Cardiac Arrest:
- Call emergency services immediately.
- Start CPR without delay.
- Use an AED (Automated External Defibrillator) if available.
- Continue until help arrives.
Quick response is key to survival in both situations. CPR and AED use can more than double survival rates in cardiac arrest symptoms cases.
Prevention and Risk Factors
While these conditions are different, they share several risk factors.
Shared Risk Factors:
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Smoking
- Poor diet
- Lack of exercise
Heart Attack-Specific Risks:
- High cholesterol
- Arterial plaque buildup
Cardiac Arrest-Specific Risks:
- Family history of arrhythmias
- Structural heart problems
- Substance abuse
Preventive care, regular check-ups, and consultations with a heart doctor near you can reduce your risk. If you’re in Gujarat, seeking advice from a Cardiologist doctor in Ahmedabad is a smart move.
Conclusion: Know the Signs, Act Fast
Understanding the difference between heart attack and cardiac arrest empowers you to respond effectively during an emergency. While both are serious and potentially fatal, timely recognition and action—whether calling emergency services, performing CPR, or getting immediate treatment—can save lives.
If you’re looking for expert heart care, consult Dr. Jignesh Patel, a highly trusted cardiologist in Ahmedabad, known for his patient-centred approach and excellence in cardiac care. Whether it’s a regular check-up or managing heart disease, choosing the right specialist is your first step toward heart health.






